

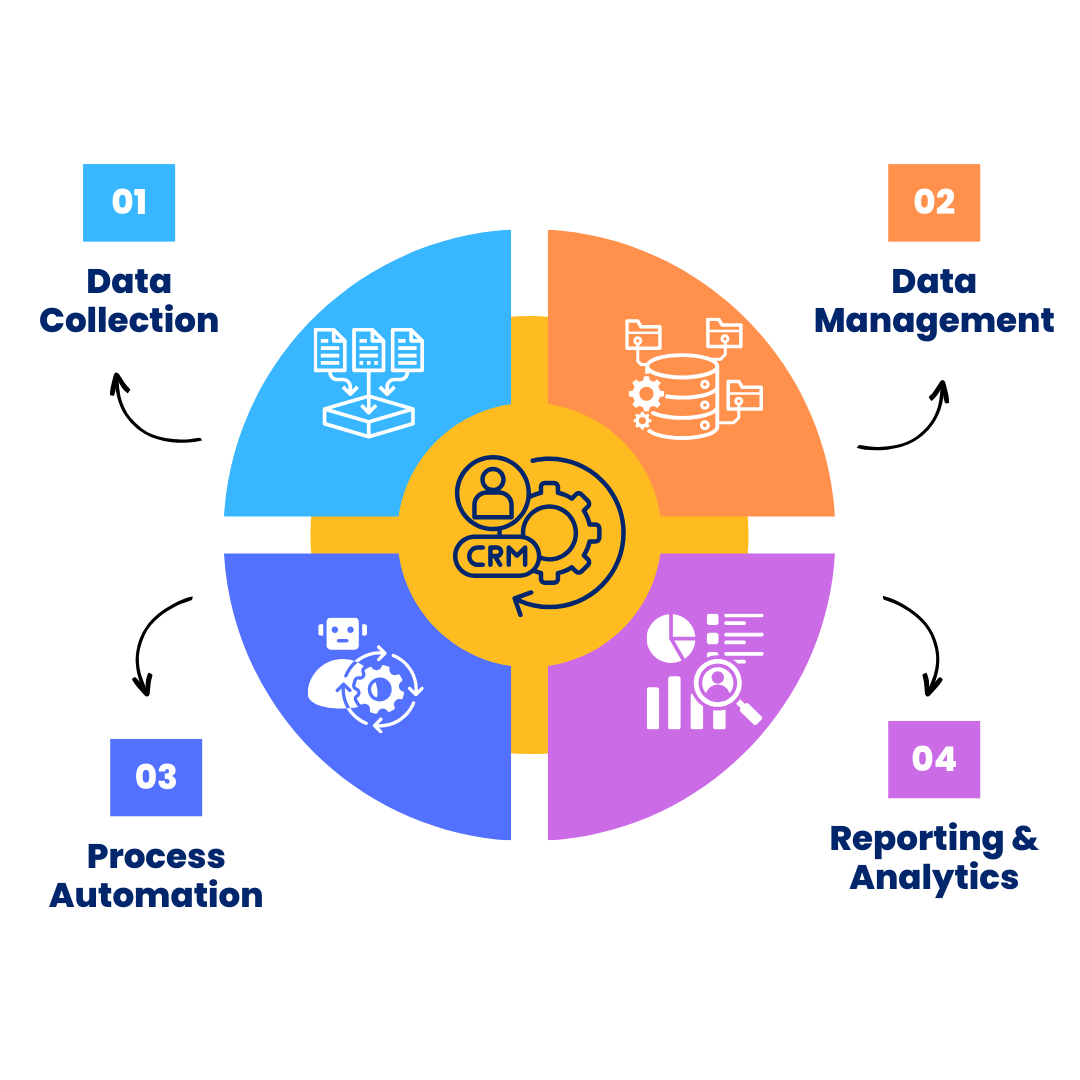
An HRMS (Human Resource Management System) and CRM (Customer Relationship Management) are two distinct but increasingly integrated types of software. While HRMS is primarily designed for managing employee data, recruitment, payroll, and performance, CRM focuses on managing customer relationships, sales, marketing, and support.
In modern business environments, many platforms integrate both HRMS and CRM functionalities to optimize employee management and customer relationship management under one umbrella. This is especially beneficial for large organizations that need to streamline HR functions while also managing customer relationships. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the working process for HRMS-CRM software:

Gathers and centralizes relevant employee and customer information from various touchpoints into a unified system.

Organizes, updates, and securely stores employee and customer data for easy access, accuracy, and compliance.

Streamlines and automates repetitive tasks such as payroll, sales follow-ups, and customer service, increasing efficiency.

Generates actionable reports and insights to measure performance, track KPIs, and support data-driven decision-making.
Centralizes and organizes employee information such as personal details, job roles, compensation, and performance history for easy access and management.
Automates payroll processes, tax calculations, deductions, and benefits administration, ensuring timely and accurate salary disbursement.
Tracks employee attendance, working hours, and manages leave requests (vacation, sick leave, etc.), integrating with payroll systems for seamless operations.
Streamlines recruitment by automating job postings, applicant tracking, interview scheduling, and employee onboarding processes to ensure a smooth entry for new hires.
Facilitates goal setting, performance reviews, and employee feedback to assess and improve individual and team performance over time.
Provides employees with an intuitive self-service portal to manage personal details, view payslips, request time off, and access HR documents, reducing HR workload.
Manages employee training programs, tracks progress, and provides learning resources to ensure employees' continuous growth and skill enhancement.
Ensures that the organization adheres to labor laws, tax regulations, health and safety standards, and other relevant compliance requirements to avoid legal risks.